How to make a good bonding
- Steps for successful bonding
- Bonding constraints to consider
- Identify the bonding surface type
- Prepare the surface before bonding
- Product tests
Quote
Close
You request has been sent.
We promise to respond to you in detail within 24 hours.
In the meantime, feel free to browse our other products.
What constraints can your bonding be subjected to ?
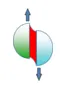
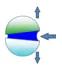
Mechanical constraints
| 
| 
| 
|
| Peeling | Tensile Strength | Shearing | Cleavage |
Whenever possible, when designing your products, give priority to tensile strength and shear strength.
Environmental constraints
An assembly is not only characterized by the nature of the forces applied to the assembly ; it is also necessary to take into account the materials to be bonded :
- High or low temperatures with the possibility of differential expansion of the assembled materials ?
- Prolonged exposure to UV rays ?
- Presence of solvents or chemical products that can make the assembly fragile ?
- Presence of plasticizers or powder coating that require an adequate adhesive ?
This list is obviously not exhaustive; each project has its own particularities and requires further study.
Constraints linked to the process
When defining the specifications, it is also imperative to take into account the constraints linked to the adhesive application process :
- Automatic or manual application ?
- Use of die-cut pieces, long-length rolls, overlapping liner to facilitate subsequent use ?
- Reduction of application time by replacing glue with an adhesive ?
- Application on worksites or in low temperatures that require specific references ?
Careful examination of the constraints linked to the process makes it easier to choose the appropriate adhesive and often allows for significant time savings during the application.
This non-exhaustive list of questions enables you to better examine the overall environment in which our adhesives are used.
Operating temperature
The temperature generally recommended for an optimal application of the adhesive is between +18 ºC and +35 ºC. In all cases, refer to the product data sheet.
Immediate adhesion (or initial tack) of adhesive is reduced at low temperatures.
Preparation of surfaces
Because even the best product applied on an oily, wet or dusty surface will never ensure a correct assembly, it is necessary to pay special attention to the state of the surfaces to assemble.
- The surface to assemble must be dry and clean.
- The elements to assemble must not be dusty and should be free of grease, oil and release agents
- If necessary, clean the surfaces with a clean, lint-free cloth and a solvent compatible with the materials.
- For the assembly of low surface energy surfaces, the use of primer can increase the bonding performance.
- The application of sufficient pressure promotes adhesion. The application of adhesive tape should be done by applying the appropriate pressure (about 10-15 N/cm2).
- The use of a masking roller or squeegee facilitates the application of the necessary pressure. Generally, adhesive tapes on thin backing material require more pressure than thicker adhesive tapes.
| Masking roller | Flexible squeegee |
 |  |
If you want to achieve high-strength structural bonding (on steel, greater than 7 Mpa), you must treat the surface of your mating surface.
Here are the main surface preparation techniques used in industry :
- Abrasion – Different methods exist like sandblasting, shot-blasting, abrasive sheets or rolls….
- Degreasing – for materials that require less preparation, a simple solvent can enable you to degrease the surface.
- Corona treatment – Suitable for Polypropylene, polyethylene and adhesion on polyolefins.
- Primer - Activator or anti-corrosion to improve overall performance.
- Chemical treatment- Commonly used for the preparation of metal ; provides the perfect surface for adhesion.
Surface conditions
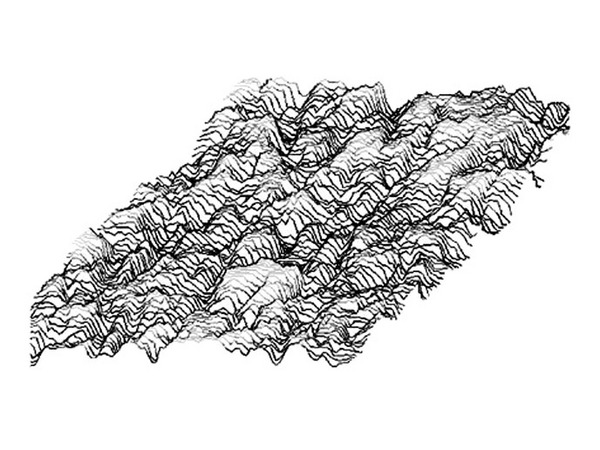
Flat surfaces promote good adhesion. Irregular surfaces require the use of thicker adhesive tapes to compensate for the irregularities of the surface to assemble.
Even a surface that appears flat to the naked eye has rough patches. The application of pressure on the adhesive tape enables to adhesive to penetrate in the irregularities of the surface.
Below, the pattern of raised rough patches on smooth steel plate.

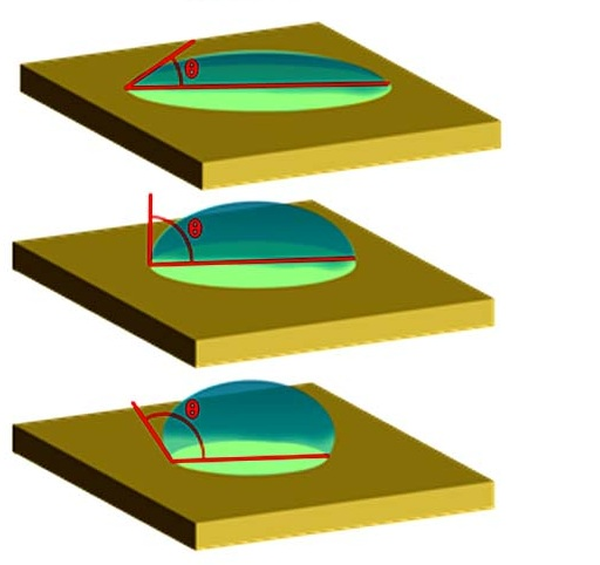
One speaks of surface energy (or surface tension) to characterize the ability of materials to be glued or bonded : Low surface energy materials are difficult to bond and require the use of an appropriate adhesive. For example, Teflon, PTFE, and Polyethylene are low surface energy materials.
|  |
Here is a list of the main materials ranked by surface energy :
- High surface energy materials, so easy to bond : copper, zinc, aluminium, tin, stainless steel, glass,
- Low surface energy materials, so difficult to bond : Polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), pva, acetal, eva, Teflon, rubber, polycarbonate, epoxy powder coating, ABS, polyvinyl chloride (PVC)....
| NATURE | MATERIALS | TECHNICAL NAME | TRADEMARK |
| Metals (High surface energie) | Copper | Cu | |
| Aluminium | Al | ||
| Zinc | Zn | ||
| Tin | Sn | ||
| stainless steel | Alloy | ||
| Lead | Pb | ||
| Glass (High surface energie) | Glass | Glass | |
Plastics with high surface energy | PI | Polyimide | Kapton |
| PA | Polyamide | Nylon - Rislan | |
| PET | Thermoplastic polyester | Alkyd | |
| PBT | Polyeterimide | Valox | |
| epoxy powder coating | |||
| PUR | Polyurethane | ||
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadienne styrene | Cycolac - Abson | |
| PC | Polycarbonate | Lexan - Makrolon - Arla | |
| Phenolic resin | |||
| PVCr | Inflexible polyvinyl chloride | Forex - Komacel | |
| PVCs | Flexible polyvinyl chloride | Stamoid - Panaflex | |
| PMMA | Polymethyl Methacrylate | Plexiglass - Acrylex - Polivar | |
| Plastics with low surface energy | PVA | Vinyl polyacetate | |
| PPO | Polyphenykene oxide | Noryl | |
| PS | Styrofoam | ||
| POM | polyacetal | Derlin | |
| EVA | EVA | ||
| PETG | Polyester | Griphen -Vectan | |
| PE | Polyethylene | ||
| PP | Polypropylene | Akylux - Ethylux | |
| PVF | Polyvinyl fluoride | Tedlar | |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene | Teflon - Dyneon |
Be careful of the following substrates ; there are traps to avoid : plasticizer migrations for flexible PVC, rust layers on metal and alloys, surface tension agents on epoxy powder coating… For each application, ask for a technical assessment to find the best double-sided adhesive tape or the best glue.
Testing and validating a product
The final adhesion is achieved 24 to 72 hours minimum after the initial contact with the surfaces to assemble. Be careful, immediate adhesion (or tack) is different from the final performance of an adhesive : an adhesive can have an average initial tack and very high final adhesion.
For bonding plastic material, it is important to consider plasticizer migrations of the surface : In particular, heat may promote plasticizer migrations.
During the validation of a product for a bonding application, be attentive to the climatic conditions that the assembly will be subjected to. When possible, try to reproduce the real conditions that the assembly will be subjected to during the validation tests.
The validation of products requires that you conduct functional tests. This validation remains the customers’ responsibility, with the assistance ADEZIF, the provision of samples and recommendations of solutions.
For further information regarding product validation, you can contact our sales teams.
Ageing
When validating a product for an application, the ageing of the assembly should be taken into account and integrated in the specifications from the beginning of the project.
Some applications require very high performance, even after ageing : automotive, rail and aeronautic applications in particular. For other applications, ageing may not be an important criterion : short-lived communication, removal of adhesive shortly after application…
Several factors can influence the performance of an assembly during ageing and should be considered carefully :
- Nature of the adhesive (Acrylic, Silicon, Rubber) backing material of the adhesive
- Nature of the assembled material. Particularly in the case of assembly of materials of different natures that have very different expansion coefficients
- Assembly subjected to shocks or under constant stress (particularly cracking and peeling constraints)
- Assembly subjected to UV rays and/or difficult climatic conditions
- Assembly subjected to extreme temperature variations
This non-exhaustive list provides an overview of the elements to consider for ageing.
Storage
Adhesive tapes should be stored at room temperature, with a normal level of humidity (50 - 70 %). The shelf life of the adhesive tape is indicated on our products’ data sheets.
Rolls should be stored flat to avoid distortion.
Adhesive storage requirements are indicated on the data sheets ; for optimal performance of your adhesive, respect the storage conditions indicated on the data sheet.
Safety data sheets
Apart from a few specific references (lead adhesive tape, for example), the Safety Data Sheets are not available.
To have the latest version of the safety data sheets, the best solution is to download them directly from the web site www.quickfds.fr